Performance
of Reynolds-Averaged Turbulence Models for Transonic Flow around Airfoil
Fluid Mechanics Laboratory, Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics,
Keywords: Reynolds-Averaged Turbulence Model, Compressible flow, Transonic Flow
Abstract
Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) simulation
continues to constitute the principal approach for representing the effects of
turbulence in the prediction of engineering flows. One issue that has been the
subject of much attention is the wall-limiting behavior returned by
low-Reynolds-number forms that are designed to be applicable across the viscous
sublayer, down to the wall.
The present study is a contribution to the ongoing search for better RANS
models. In this study, several RANS models are investigated, including some recently-developed
non-linear eddy-viscosity models. To examine the model performance for
compressible flow applications, they are applied to a transonic flow around an
airfoil. Sample results are shown in Fig. 1. The obtained results are compared
with the corresponding experimental data by Schmitt
and Charpin[1].
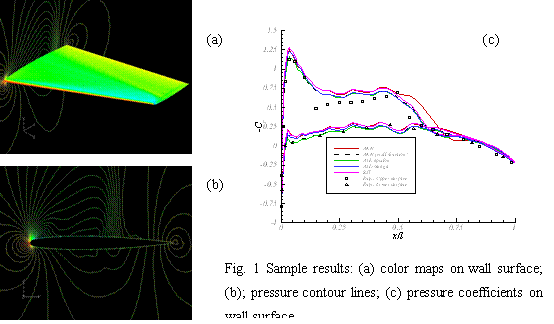
More detailed discussion is given in the reference paper[2].
References
[1] V. Schmitt. and F. Charpin, Pressure Distributions
on the ONERA-M6-Wing at Transonic Mach Numbers, Experimental Data Base for
Computer Program Assessment, Report
of the Fluid Dynamics Panel Working Group 04, AGARD AR 138, May 1979.
[2] Kentaro HARA and Ken-ichi
ABE, Performance
of Reynolds-Averaged Turbulence Models for Transonic Flow around Airfoil, Progress in Computational Fluid
Dynamics, Vol. 8, pp. 447-453, 2008.
All Rights Reserved,
Copyright(C) 2008, Fluid Mechanics Laboratory,
Department of Aeronautics
and Astronautics,